Most people have heard the terms “hard water” and “soft water,” but few actually know the difference between the two. Even fewer people know what do about their water if they find out that it is excessively hard or soft. We have you covered in this article.
1. Make the diagnosis
In general, it is much easier to spot hard water. That’s because hard water leaves very visible clues. Hard water is characterized by abnormally high mineral content. For example, if you look at the photo at the beginning of the post, you will see mineral residue that rings the drain.
If you don’t see any evidence of mineral residue, there is another test you can perform to determine if you have hard water:
- Bring a cup of water almost to a boil (you can heat the water in the microwave if you’d like).
- Now let the water settle for a minute.
- Look at the surface of the water, if you notice that it is cloudy or that there is a thin film across the top, this is a good indication that you have hard water.
Determining that you have soft water is more difficult. That’s because soft water does not leave visible clues. To determine if you have soft water, your best bet is to pick up a water testing kit at your local hardware store. They are cheap, reliable and easy to use.
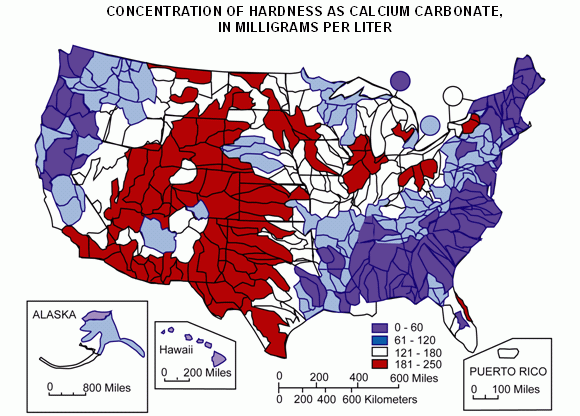
This map indicates the general presence of hard and soft water in the United States:
Source: USGS
What do you do if you have hard or soft water?
Ok, so you have determined that you have hard or soft water. Now what? Well, the first thing we need to find out is whether or not the water is safe to drink.
In general, soft water is worse than hard water in terms of drinking water. In terms of laundry and showering, soft water is preferred, as it is less corrosive. However, soft water leeches minerals from wherever it can. This means that your drinking water could be pulling contaminants from your pipes and elsewhere before you drink it. Obviously, this is a huge problem if you have lead anywhere in your piping.
If soft water is worse for drinking than hard water, what can you do about it? There are a few possibilities. One thing you can do is to install a water hardener, which generally uses chemicals to harden the water. Another option – our preferred option – would be to install a reverse osmosis system (see our recommended system here). Reverse osmosis systems allow you to hit the reset button on your water. They filter out all the impurities, and if you have a good system like the one we recommend, the water will be remineralized with the proper levels of calcium and magnesium.
So does that mean hard water is not harmful? In general, hard water is not an issue in terms of drinking water. In fact, those who drink moderately hard water have been shown to have lower rates of cardiovascular disease over the course of their lives. This is due to the supplemental calcium and magnesium provided by the water. However, when the mineral content is abnormally excessive, you will have problems maintaining your pipes and any appliance that works with water.
If you do have excessively hard water, you can install a water softener. However, like water hardeners, we would caution against a softener. Softeners often remove too many minerals while also adding sodium to the water (sodium ion beads are typically used to demineralize the water, and as a result, your drinking water will have higher quantities of sodium).
Once again, we would recommend a RO system. Remember, this is only if your water is excessively hard, and it is noticeably corroding your pipes and damaging your water-related appliances. If it is moderately hard, enjoy the extra minerals – they are good for you!





{ 0 comments… add one }